RESEARCH
Field-tested in a sample of 2233 patients ages 8 to 29 years with cleft and noncleft conditions.
FACE-Q Craniofacial is a rigorously developed patient-reported outcome measure that can be used to collect and compare evidence-based outcomes data from patients aged 8 to 29 years with a visible and/or functional facial difference. For patients with facial paralysis, there is no upper age limit. This FACE-Q module was developed from concept elicitation interviews with 84 patients with 28 different congenital and acquired conditions (e.g., microtia, facial paralysis, craniosynostosis, craniofacial microsomia). The qualitative study was followed by an international field-test study that recruited 2233 patients aged 8 to 29 years with a broad range of craniofacial conditions.

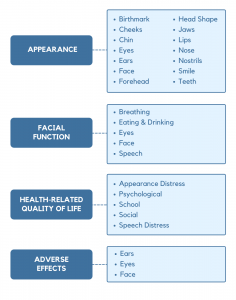
The conceptual framework for FACE-Q Craniofacial covers 4 domains: appearance, function, health-related quality of life, and adverse effects. Each domain is composed of multiple independently functioning scales. The variety of scales provides flexibility to choose the subset of scales best suited to measure the outcomes of interest in any given study or clinical situation.
FACE-Q Craniofacial module includes 27 scales/checklists that can be used to evaluate treatment outcomes for patients aged 8 to 29 years with any type of craniofacial condition. Clinicians and researchers are able to administer the subset of scales relevant to their situation.
Fourteen scales measure aspects of appearance including the face overall, specific parts of the face, and smile. For the birthmark scale, the field-test study included patients with a birthmark anywhere on the face or body.
Five scales/checklists measure facial functions, including breathing, eating/drinking, functions involving the eye (e.g., blink, see properly) and face (e.g., smile, frown), as well as speaking.
Five scales measure aspects of health-related quality of life, including appearance-related distress, speech distress, as well as psychological, social, and school function.
Three checklists measure adverse effects (e.g., numbness, pain, swelling, itchy) following surgery, including eyes, ears, and face.