Research
Field-tested with 657 participants from the US, Canada and UK.
As more people access an increasing range of treatments to rejuvenate their appearance and improve their quality of life, it is vital that outcomes are carefully evaluated. The SKIN-Q is an innovative PROM designed to evaluate outcomes of minimally invasive aesthetic treatments of the face and body. Concept elicitation data from 26 participants was used to form 2 item libraries that measure satisfaction with how someone’s skin looks and feels. Input from 12 experts, 11 patients and 189 online participants was used to finalize a version of the SKIN-Q for field testing. Psychometric analysis was performed on 713 field test surveys (facial skin, n = 496 and body skin, n = 174). A subset of participants completed a test-retest study.

The SKIN-Q represents 2 comprehensive item libraries designed to measure how the skin feels and looks. The design of SKIN-Q makes it possible for end-users to customize fit-for-purpose short-form scales to maximize content validity and reduce patient burden. More specifically, sub-sets of items can be selected from an item set and scored by calibrating scores to the full set of items (i.e., item-bank approach), or scored using estimates from independent samples (i.e., item-library approach). From the set of items, we published 5 example short-form scales that can be used to measure skin-related concerns (eg, skin quality, rejuvenation).
Field-tested with 657 participants from the US, Canada and UK.
Can be used in clinical trials of minimally invasive aesthetic treatments (face or body).
Designed using a modern psychometric approach to facilitate use in patient care.
While standard practice for PROM design involves the development of short-form scales composed of a limited set of items, more recently, item libraries and item banks have been developed to provide a flexible approach to scale design. To evaluate outcomes for aesthetic treatments that target the skin, we developed a comprehensive set of items to measure satisfaction with how the skin feels and looks and provide a way to customize fit-for-purpose scales. In this approach, sub-sets of items can be selected from an item set and scored by calibrating scores to the full set of items (i.e., item-bank approach), or scored using estimates from independent samples (i.e., item-library approach). The short-form approach aims to minimize respondent burden while maximizing content validity.
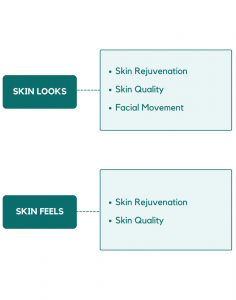
SKIN-Q includes 46 items that measure satisfaction with how skin on the body and/or face looks. Three short-form scales were created to illustrate the use of the item library. The first scale includes 7 items that ask about facial movement (e.g., smile, show expression, raise eyebrows, frown). The second scale includes 9 items that measure skin rejuvenation (e.g., youthful, glow, radiant, healthy, fresh). The third scale includes 12 items that measure skin quality (e.g., firm, smooth, hydrated, elasticity).
The SKIN-Q includes 20 items that measure satisfaction with how skin on the face and/or body feels. Two example short-form scales were created to illustrate the use of the item set. The first scale includes 6 items that measures skin rejuvenation (e.g., youthful, refreshed, rejuvenated, healthy). The second scale includes 9 items that measures skin quality (e.g., firm, elasticity, hydrated, smooth).